CNN网络中池化层的正向传播与反向传播理解
日期: 2018-05-23 分类: 个人收藏 492次阅读
1. 池化定义
通常来说卷积之后的图像虽然在尺寸上有所减小,但是其尺寸还是较大,为了描述大的图像,一个很自然的想法就是对不同位置的特征进行聚合统计,例如,人们可以计算图像一个区域上的某个特定特征的平均值 (或最大值)。这些概要统计特征不仅具有低得多的维度 (相比使用所有提取得到的特征),同时还会改善结果(不容易过拟合)。这种聚合的操作就叫做池化 (pooling),有时也称为平均池化或者最大池化 (取决于计算池化的方法)。
池化的不变性:如果人们选择图像中的连续范围作为池化区域,并且只是池化相同(重复)的隐藏单元产生的特征,那么,这些池化单元就具有平移不变性 (translation invariant)。这就意味着即使图像经历了一个小的平移之后,依然会产生相同的 (池化的) 特征。使得网络具有了一定的鲁棒性。
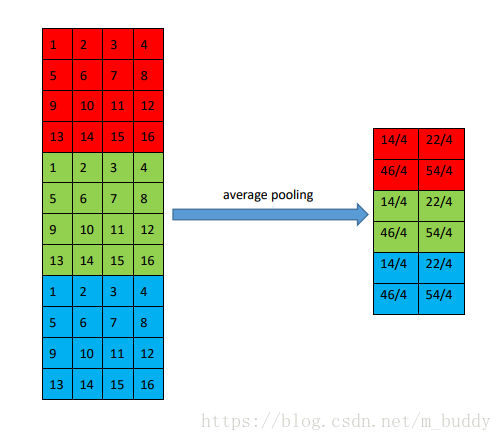
下面一幅图就是对池化层的形象描述。

池化层之后的矩阵数据一般会大小减半,但是其减半的方式也主要有两种Max-Pooling和Average-Pooling。
2. 池化层正向传播
2.1 Max-Pooling
该种类型的池化层是取运算窗口中的最大值作为最后运算的结果,可以表示为:
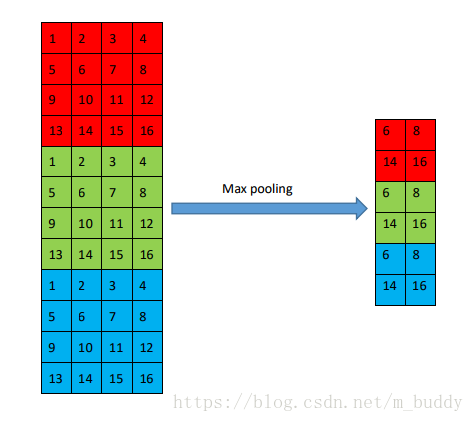
上图中就是以
3∗2
3
∗
2
大小的窗口进行运算得到的结果
2.2 Average-Pooling
该种类型的池化层是取运算窗口中的所有值的均值作为最后运算的结果,可以表示为:
2.3 Caffe代码
template <typename Dtype>
void PoolingLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
Dtype* top_data = top[0]->mutable_cpu_data();
const int top_count = top[0]->count();
// We'll output the mask to top[1] if it's of size >1.
const bool use_top_mask = top.size() > 1;
int* mask = NULL; // suppress warnings about uninitalized variables
Dtype* top_mask = NULL;
// Different pooling methods. We explicitly do the switch outside the for
// loop to save time, although this results in more code.
switch (this->layer_param_.pooling_param().pool()) {
case PoolingParameter_PoolMethod_MAX: //Max-Pooling
// Initialize
if (use_top_mask) {
top_mask = top[1]->mutable_cpu_data();
caffe_set(top_count, Dtype(-1), top_mask);
} else {
mask = max_idx_.mutable_cpu_data();
caffe_set(top_count, -1, mask);
}
caffe_set(top_count, Dtype(-FLT_MAX), top_data);
// The main loop
for (int n = 0; n < bottom[0]->num(); ++n) {
for (int c = 0; c < channels_; ++c) {
for (int ph = 0; ph < pooled_height_; ++ph) {
for (int pw = 0; pw < pooled_width_; ++pw) {
int hstart = ph * stride_h_ - pad_h_;
int wstart = pw * stride_w_ - pad_w_;
int hend = min(hstart + kernel_h_, height_);
int wend = min(wstart + kernel_w_, width_);
hstart = max(hstart, 0);
wstart = max(wstart, 0);
const int pool_index = ph * pooled_width_ + pw;
//计算当前窗口的最大值,作为最后的结果
for (int h = hstart; h < hend; ++h) {
for (int w = wstart; w < wend; ++w) {
const int index = h * width_ + w;
if (bottom_data[index] > top_data[pool_index]) {
top_data[pool_index] = bottom_data[index];
if (use_top_mask) {
top_mask[pool_index] = static_cast<Dtype>(index);
} else {
mask[pool_index] = index;
}
}
}
}
}
}
// compute offset
bottom_data += bottom[0]->offset(0, 1);
top_data += top[0]->offset(0, 1);
if (use_top_mask) {
top_mask += top[0]->offset(0, 1);
} else {
mask += top[0]->offset(0, 1);
}
}
}
break;
case PoolingParameter_PoolMethod_AVE: // Average-Pooling
for (int i = 0; i < top_count; ++i) {
top_data[i] = 0;
}
// The main loop
for (int n = 0; n < bottom[0]->num(); ++n) {
for (int c = 0; c < channels_; ++c) {
for (int ph = 0; ph < pooled_height_; ++ph) {
for (int pw = 0; pw < pooled_width_; ++pw) {
//计算窗口中所有元素的均值作为最后的结果
int hstart = ph * stride_h_ - pad_h_;
int wstart = pw * stride_w_ - pad_w_;
int hend = min(hstart + kernel_h_, height_ + pad_h_);
int wend = min(wstart + kernel_w_, width_ + pad_w_);
int pool_size = (hend - hstart) * (wend - wstart);
hstart = max(hstart, 0);
wstart = max(wstart, 0);
hend = min(hend, height_);
wend = min(wend, width_);
for (int h = hstart; h < hend; ++h) {
for (int w = wstart; w < wend; ++w) {
top_data[ph * pooled_width_ + pw] +=
bottom_data[h * width_ + w];
}
}
top_data[ph * pooled_width_ + pw] /= pool_size;
}
}
// compute offset
bottom_data += bottom[0]->offset(0, 1);
top_data += top[0]->offset(0, 1);
}
}
break;
case PoolingParameter_PoolMethod_STOCHASTIC:
NOT_IMPLEMENTED;
break;
default:
LOG(FATAL) << "Unknown pooling method.";
}
}3. 池化成反向传播
池化层一般没有参数,所以反向传播的时候,只需对输入参数求导,不需要进行权值更新。但是具体在计算的时候是要根据Max还是Average来进行区分,进行参数更新的。
3.1 Max-Pooling
如果只看输出矩阵中的一个点y,则有 y = max( x1 , x2, x3, … )。所以对x求导后有(可以理解成分段函数的求导),则有

也就是寻找顶层与下层之间的映射关系,之后将上层的结果添加到下层中去。
for (int ph = 0; ph < pooled_height_; ++ph) {
for (int pw = 0; pw < pooled_width_; ++pw) {
const int index = ph * pooled_width_ + pw;
const int bottom_index =
use_top_mask ? top_mask[index] : mask[index];
bottom_diff[bottom_index] += top_diff[index];
}
}这个xn如果影响多个y,则会叠加起来。具体来说可以使用下面这幅图片进行说明
3.2 Average-Pooling
如果只看输出矩阵中的一个点y,则有 y = ( x1 , x2, x3, … ,xn )/n。所以对x求导后有

也就是映射过去之后去均值
for (int h = hstart; h < hend; ++h) {
for (int w = wstart; w < wend; ++w) {
bottom_diff[h * width_ + w] +=
top_diff[ph * pooled_width_ + pw] / pool_size;
}
}具体来说可以使用下面这幅图片进行说明
3.3 Caffe中的完整代码实现
template <typename Dtype>
void PoolingLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
if (!propagate_down[0]) {
return;
}
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->cpu_diff();
Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[0]->mutable_cpu_diff();
// Different pooling methods. We explicitly do the switch outside the for
// loop to save time, although this results in more codes.
caffe_set(bottom[0]->count(), Dtype(0), bottom_diff);
// We'll output the mask to top[1] if it's of size >1.
const bool use_top_mask = top.size() > 1;
const int* mask = NULL; // suppress warnings about uninitialized variables
const Dtype* top_mask = NULL;
switch (this->layer_param_.pooling_param().pool()) {
case PoolingParameter_PoolMethod_MAX:
// The main loop
if (use_top_mask) {
top_mask = top[1]->cpu_data();
} else {
mask = max_idx_.cpu_data();
}
for (int n = 0; n < top[0]->num(); ++n) {
for (int c = 0; c < channels_; ++c) {
for (int ph = 0; ph < pooled_height_; ++ph) {
for (int pw = 0; pw < pooled_width_; ++pw) {
const int index = ph * pooled_width_ + pw;
const int bottom_index =
use_top_mask ? top_mask[index] : mask[index];
bottom_diff[bottom_index] += top_diff[index];
}
}
bottom_diff += bottom[0]->offset(0, 1);
top_diff += top[0]->offset(0, 1);
if (use_top_mask) {
top_mask += top[0]->offset(0, 1);
} else {
mask += top[0]->offset(0, 1);
}
}
}
break;
case PoolingParameter_PoolMethod_AVE:
// The main loop
for (int n = 0; n < top[0]->num(); ++n) {
for (int c = 0; c < channels_; ++c) {
for (int ph = 0; ph < pooled_height_; ++ph) {
for (int pw = 0; pw < pooled_width_; ++pw) {
int hstart = ph * stride_h_ - pad_h_;
int wstart = pw * stride_w_ - pad_w_;
int hend = min(hstart + kernel_h_, height_ + pad_h_);
int wend = min(wstart + kernel_w_, width_ + pad_w_);
int pool_size = (hend - hstart) * (wend - wstart);
hstart = max(hstart, 0);
wstart = max(wstart, 0);
hend = min(hend, height_);
wend = min(wend, width_);
for (int h = hstart; h < hend; ++h) {
for (int w = wstart; w < wend; ++w) {
bottom_diff[h * width_ + w] +=
top_diff[ph * pooled_width_ + pw] / pool_size;
}
}
}
}
// offset
bottom_diff += bottom[0]->offset(0, 1);
top_diff += top[0]->offset(0, 1);
}
}
break;
case PoolingParameter_PoolMethod_STOCHASTIC:
NOT_IMPLEMENTED;
break;
default:
LOG(FATAL) << "Unknown pooling method.";
}
}4. 参考资料
标签:[5] 机器学习 池化层
上一篇: shell编程——变量和引用
下一篇: python编码转换
精华推荐